一、概述
类定义:
public final class Long extends Number implements Comparable<Long>
是对基本数据类型long的包装。
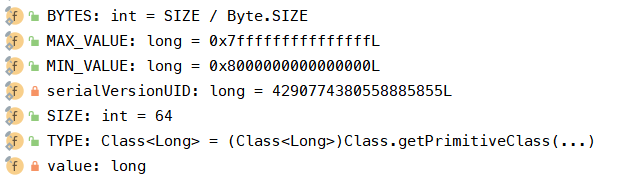
二、主要属性
三、主要方法及其源码
1.toString相关的
public static String toString(long i, int radix)
public static String toUnsignedString(long i, int radix)
private static BigInteger toUnsignedBigInteger(long i)
public static String toHexString(long i)
public static String toOctalString(long i)
public static String toBinaryString(long i)
public static String toString(long i)
public static String toUnsignedString(long i)
里面几个无修饰符和私有方法:
private static BigInteger toUnsignedBigInteger(long i) {
if (i >= 0L)
return BigInteger.valueOf(i);
else {
int upper = (int) (i >>> 32);
int lower = (int) i;
// return (upper << 32) + lower
return (BigInteger.valueOf(Integer.toUnsignedLong(upper))).shiftLeft(32).
add(BigInteger.valueOf(Integer.toUnsignedLong(lower)));
}
}
static String toUnsignedString0(long val, int shift) {
// assert shift > 0 && shift <=5 : "Illegal shift value";
int mag = Long.SIZE - Long.numberOfLeadingZeros(val);
int chars = Math.max(((mag + (shift - 1)) / shift), 1);
char[] buf = new char[chars];
formatUnsignedLong(val, shift, buf, 0, chars);
return new String(buf, true);
}
static int formatUnsignedLong(long val, int shift, char[] buf, int offset, int len) {
int charPos = len;
int radix = 1 << shift;
int mask = radix - 1;
do {
buf[offset + --charPos] = Integer.digits[((int) val) & mask];
val >>>= shift;
} while (val != 0 && charPos > 0);
return charPos;
}
static void getChars(long i, int index, char[] buf) {
long q;
int r;
int charPos = index;
char sign = 0;
if (i < 0) {
sign = '-';
i = -i;
}
// Get 2 digits/iteration using longs until quotient fits into an int
while (i > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
q = i / 100;
// really: r = i - (q * 100);
r = (int)(i - ((q << 6) + (q << 5) + (q << 2)));
i = q;
buf[--charPos] = Integer.DigitOnes[r];
buf[--charPos] = Integer.DigitTens[r];
}
// Get 2 digits/iteration using ints
int q2;
int i2 = (int)i;
while (i2 >= 65536) {
q2 = i2 / 100;
// really: r = i2 - (q * 100);
r = i2 - ((q2 << 6) + (q2 << 5) + (q2 << 2));
i2 = q2;
buf[--charPos] = Integer.DigitOnes[r];
buf[--charPos] = Integer.DigitTens[r];
}
// Fall thru to fast mode for smaller numbers
// assert(i2 <= 65536, i2);
for (;;) {
q2 = (i2 * 52429) >>> (16+3);
r = i2 - ((q2 << 3) + (q2 << 1)); // r = i2-(q2*10) ...
buf[--charPos] = Integer.digits[r];
i2 = q2;
if (i2 == 0) break;
}
if (sign != 0) {
buf[--charPos] = sign;
}
}
这些方法用到了Integer的几个属性,还使用了了一些移位操作。
2.parseLong
public static long parseLong(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException
{
if (s == null) {
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
}
if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
}
long result = 0;
boolean negative = false;
int i = 0, len = s.length();
long limit = -Long.MAX_VALUE;
long multmin;
int digit;
if (len > 0) {
char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"
if (firstChar == '-') {
negative = true;
limit = Long.MIN_VALUE;
} else if (firstChar != '+')
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
if (len == 1) // Cannot have lone "+" or "-"
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
i++;
}
multmin = limit / radix;
while (i < len) {
// Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix);
if (digit < 0) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
if (result < multmin) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
result *= radix;
if (result < limit + digit) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
result -= digit;
}
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
return negative ? result : -result;
}
四、Short
Long和Short中有些方法已经在Integer中进行了讲解,所以不再赘述。Short中的最小最大属性如下:
public static final short MIN_VALUE = -32768;
public static final short MAX_VALUE = 32767;
版权声明:本文不是「本站」原创文章,版权归原作者所有 | 原文地址: